Getting Started with Core Banking
After performing the installation process, Core Banking needs a series of configurations to be put in place before being ready for production. For example, it needs records for the main bank that uses the system, reconciliation accounts to be used for transactions, exchange rates information, holidays to be declared, specific settings for the Core Banking system parameters that indicate how the system should handle different situations or perform specific calculations, and so on.
This page is a step-by-step guide about what you have to set up, with links to detailed instructional pages related to each specific step. Follow through these steps after installing Core Banking and before declaring it ready for production.
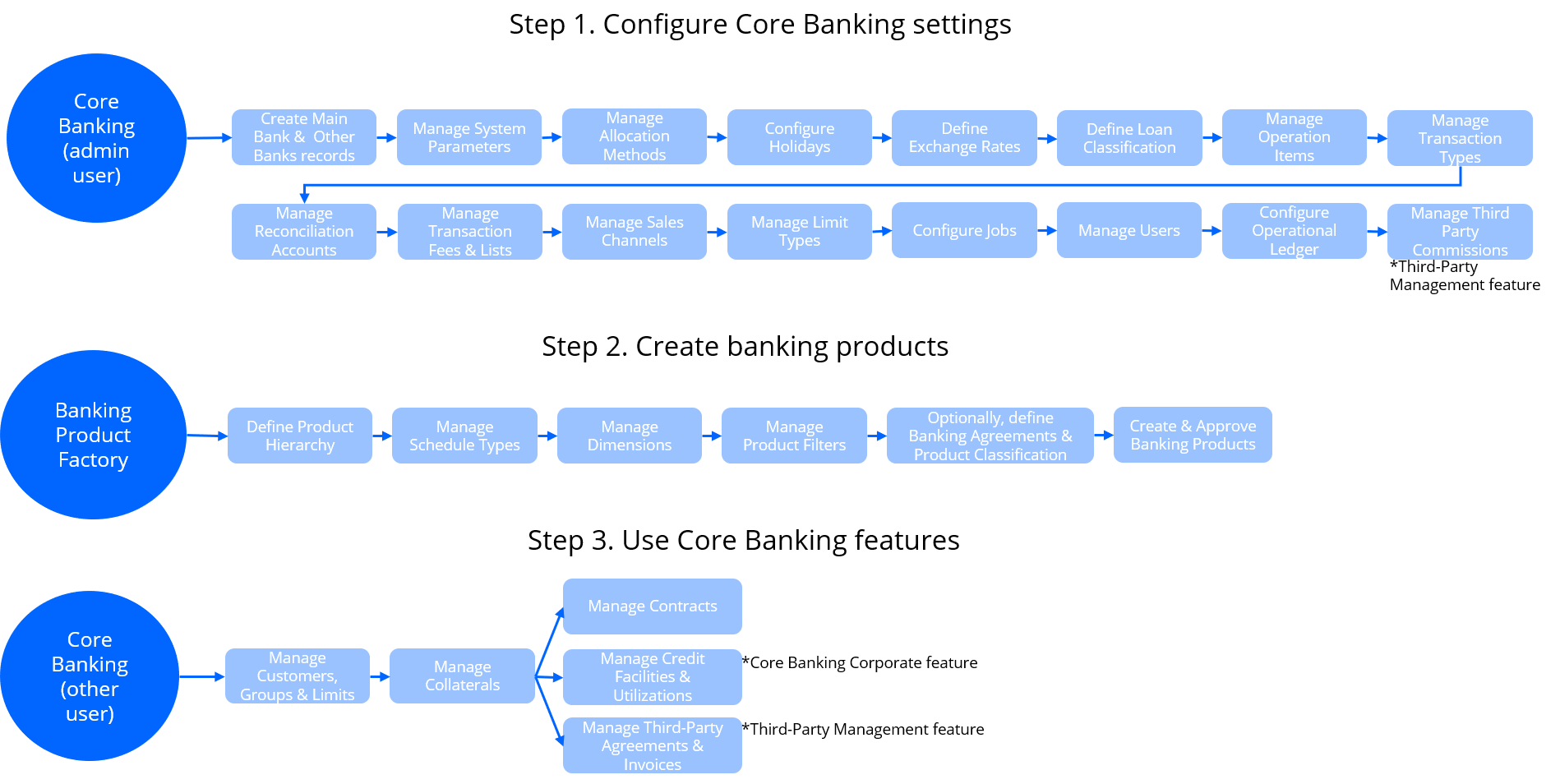
Follow these steps to configure the settings needed by Core Banking:
-
Log into FintechOS Portal using a user with administrator rights.
The user credentials for an administrator user are received from your FintechOS contact person. Insert the user name and the password associated with it to log into the FintechOS Portal. -
Define your main bank.
You must create a bank record to be used by Core Banking as the main financial institution. Use the Core Banking Operational > Bank menu and make sure the record has theMain Bankcheckbox selected. -
Manage your Core Banking system parameters.
The system parameters used by Core Banking determine the behavior of all the contracts, transactions, limits, and other parts that make up your Core Banking system. See here the list of system parameters used by Core Banking, along with their descriptions. -
Manage allocation methods.
Core Banking uses allocation methods to determine the order in which credit items are prioritized when repaying loans, credit accounts, etc. Read here how to create and manage allocation methods, using the Allocation Method menu. -
Enter holidays for the desired countries.
Public holidays for each country are used in the product definition for the calendar years over which your financial institution's current business is spread. Use the Holiday menu to create holiday records specific to your financial institution's needs, as described here. -
Define exchange rate types and enter exchange rate records.
Exchange rates represent the value between the currencies of two countries on a given date. These rates are free-floating or fixed. Add exchange rate types using the Exchange Rate Type menu if you need to differentiate between exchange rates based on the currency market or business area. Read more information about creating exchange rate records and managing exchange rate types. -
Define your loan classification.
Financial institutions classify their existing loan contracts based upon the days past due (DPD), the number of days passed since repayment due date without fully repaying the due amount. Since the provisions have an impact on the financial results of the bank, this is again driven by regulations and may vary in time or depending on country or region. Create loan classification records as described here. -
Manage operation items specific for your business.
Operation items are those items that relate to a bank's core business, such as all types of fees, commissions, principals, interests, advances, or penalty calculations. They can also be considered as balance types that add up to a certain deal or used in tracing what happened on a particular deal. Find here examples and information on creating operation item records. -
Manage transaction types.
Any transfer of funds between two bank accounts is recorded as a transaction. The transaction types are predefined for usage within Core Banking processes. Read here about different types of transactions used in Core Banking. -
Define other banks or financial institutions with whom your main bank has business relations and add external accounts.
Create bank records for the banking institutions with whom your main bank collaborates, using the Core Banking Operational > Bank menu. Add external bank accounts within these banks. -
Define reconciliation accounts and default settings for the reconciliation accounts.
Reconciliation is an accounting process that compares two sets of records to check that figures are correct and in agreement. Learn here how to manage the reconciliation accounts records. Read about setting up which reconciliation account for a specified currency should be used by Core Banking within a given period. -
Manage transaction fees and lists.
You can define different fees to be applied to bank account transactions. Using fee lists, you can attach fees with specified values to each bank account transaction operation type. When a transaction operation type is selected on a bank account transaction, Core Banking identifies the fee list and fee values and applies them considering the current date of the transaction. -
Define sales channels for your contracts.
You can create contracts through different channels:, such as the dedicated Core Banking menus in FintechOS Portal, API integration calls, or various customer journeys implemented within FintechOS accelerators. Manage the sales channels records, so that you can apply different pricing or to allow the selling a product on a specific channel. -
Manage limit types for role-based limits.
You can create new limit types that are based on roles associated to contract participants specific to your business, and use them throughout Core Banking with all the functionality of any other default limit type. -
Make sure a JobServer is up and running.
To perform the processes within Core Banking, a JobServer must be up and running. Manage server jobs as described here. Learn here about Core Banking's scheduled jobs. -
Create users and allocate them appropriate security roles.
For appropriate access and rights within Core Banking, create users and allocate them appropriate Core Banking security roles. The following pages contain information related to this topic: Adding Users, Editing Users, and Security Roles. -
Configure Operational Ledger. The Operational Ledger Add-On, installed over the Core Banking package, manages the accounting information needed for ledger reports and other financial statements. Access the Configurations page for information about the settings you need to perform.
-
Perform third-party configurations.
If you installed the Third-Party Management package on top of the Core Banking package, you should configure the schemas, types and commissions that Core Banking should apply to the agreements recorded for third-party entities.
Use Banking Product Factory to create the banking products that your financial institution wants to offer to their customers via contracts. Core Banking integrates directly with Banking Product Factory, thus all the banking products with Active status are automatically available for you to use in Core Banking, when you create contracts. Before actually creating the banking products, you should perform a series of configurations within Banking Product Factory.
Once you install Core Banking, Banking Product Factory enhances with another section, the Lean Core Settings tab at the banking product level, that gives additional configuration ability to the banking product.
After configuring the Core Banking settings and creating banking products, you are ready to use the main features available in Core Banking, as described in the following steps:
-
Log into FintechOS Portal using a user with an associated Core Banking security role.
Insert the user name and the password associated with it to log into the FintechOS Portal. -
Add customers and groups, then set customer limits.
Financial institutions deal with customers, either individuals or legal entities. Customers may be part of groups. In Core Banking, create customer records and attach them to groups. Monitor your financial institution's exposure for credit related activities by setting up limits for your customers. You can manage limits through a series of menus and reports available in Core Banking. -
Register collaterals.
Collateral management is the method of granting, verifying and managing collateral transactions in order to reduce credit risk in unsecured financial transactions. It is an essential and integral part of any financial institution's risk and regulatory compliance framework. Manage collateral records in Core Banking, as described here. -
Manage contracts.
Any agreement between a financial institution and a customer regarding the usage of a banking product is documented legally with a contract. In Core Banking, you can create contracts for your financial institution's customers based on approvals. Read about contracts in the Contracts page. -
Manage credit facilities.
Credit facilities are groupings of multiple credit products that a customer has arranged with a bank under a single credit limit. Read here how to manage credit facility records.
The credit facility management features are available only if the Core Banking Corporate package was installed. -
Manage third-party agreements & invoices.
In Core Banking, you can register third-party entities (agents, brokers, insurers, etc.) with the financial institution to intermediate the selling of various banking products to customers. For their work, the third-party entities are compensated with fees payable for each new contract, based on a pricing agreement with the financial institution. Read here how to manage records related to third-party entities.
The third-party management features are available only if the Third-Party Management package was installed.